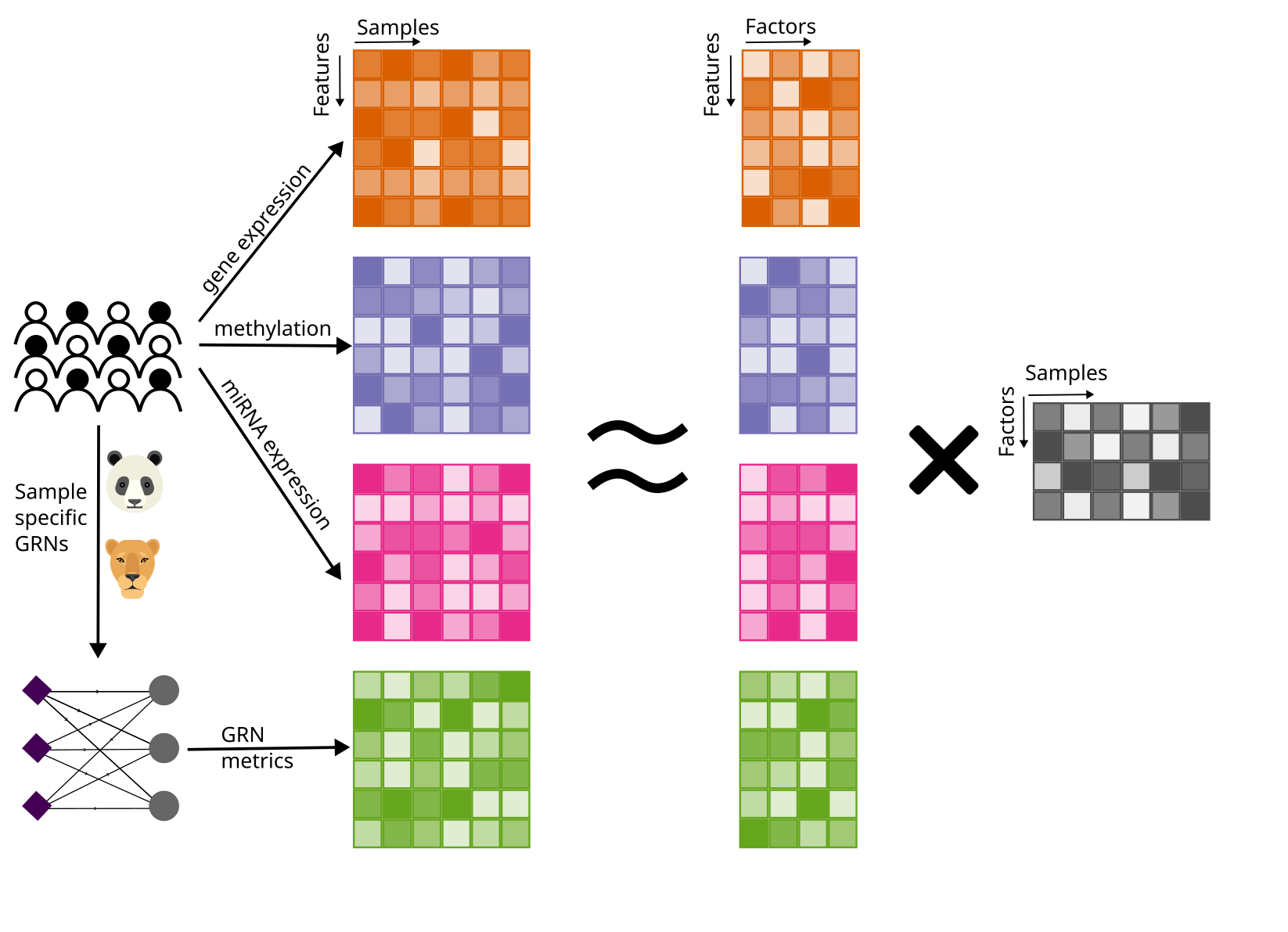New bioRχiv pre-print
We have a new BioRχiv pre-print by Romana, in which we present MARMOT, a novel approach to integrating patient-specific gene regulatory network models (GRNs) with multi-omics data to enhance cancer survival predictions.
Cancer is complex, with disruptions at multiple molecular levels. In this study, we explore how patient-specific gene regulatory networks—models of transcriptional regulation—can improve patient-specific insights when integrated with multi-omics data.
Multi-modal data often have widely different dimensions (e.g., gene expression vs. methylation vs. networks), complicating joint analysis. To address this, we developed a PCA-based framework that harmonizes these data types prior to data integration. We used this approach to combine patient-specific gene regulatory networks with multi-omics data across ten cancer types with joint dimensionality reduction (JDR) approaches. We benchmarked whether including networks could improve the detection of meaningful associations with clinical features, such as patient survival, and found that including network metrics enabled improved sensitivity in identifying survival-associated factors in multiple cancer types.
We independently validated findings in liver cancer, for which we could detect three multi-omics factors associated with survival. These factors were linked to dysregulation of metabolic pathways, including fatty acid metabolism, in multiple cohorts, and linked to JUND as a potential upstream transcriptional regulator.
Our method highlights the importance of incorporating GRN features into multi-omics analyses to enhance our understanding of cancer mechanisms at the individual patient level. This approach holds potential for advancing personalized diagnostics and therapies in the future.
To ensure our findings are accessible and reproducible, we provide:
- A contained and input data on Zenodo.
- Code to reproduce all analyses on GitHub.
- Our analysis package MARMOT.
More information on the pre-print can be found here.